- Full width
- Box
Process Cooling Solutions
Industrial process cooling solutions refer to the various methods and technologies used to remove excess heat generated during industrial processes. Efficient process cooling is essential to maintain optimal operating conditions, product quality, and equipment reliability in industries such as manufacturing, chemical processing, power generation, and more. Different cooling solutions are available based on the specific requirements of each industrial process. Some common industrial process cooling solutions include.
We are Services / Solutions Provider of Process Cooling Solutions / Systems, Chiller Systems, Cooling Towers, Air Cooled Heat Exchangers, Water Cooled Heat Exchangers, DX Cooling Systems, Evaporative Cooling Systems, Cryogenic Cooling and our setup is in Pune, Maharashtra, India
Chiller Systems :
Chiller systems use refrigeration technology to cool liquids, which are then circulated through heat exchangers to remove heat from industrial equipment or processes. They are versatile and widely used for various applications.Cooling Towers :
Cooling towers use the principle of evaporative cooling to remove heat from water or other fluids. Hot process fluids are circulated through the tower, where a portion of the fluid is evaporated, transferring heat and cooling the remaining fluid.Air-Cooled Heat Exchangers :
These heat exchangers transfer heat from industrial processes to ambient air. They consist of finned tubes through which process fluids flow, and a fan blows air across the fins to dissipate heat.Water-Cooled Heat Exchangers :
Water-cooled heat exchangers use a water supply to cool industrial fluids. The process fluid is passed through tubes, and a separate water stream removes heat by flowing around the tubes.Direct Expansion (DX) Cooling :
DX cooling systems use refrigerants to directly cool air in industrial spaces. They are commonly used in smaller applications where localized cooling is required.Evaporative Cooling Systems :
Evaporative cooling systems use the principle of water evaporation to cool air. They are effective in dry climates and are used in applications where air temperature reduction is essential.Cryogenic Cooling :
Cryogenic cooling involves the use of very low-temperature gases or liquids, such as liquid nitrogen, to rapidly cool industrial processes or equipment.Heat Recovery Systems :
Heat recovery systems capture waste heat from industrial processes and repurpose it for other heating needs or to generate power.Hybrid Cooling Solutions :
Hybrid solutions combine multiple cooling technologies to optimize efficiency and performance. For example, combining air cooling with evaporative cooling can enhance overall cooling efficiency.Process Fluid Cooling :
In industries such as chemical manufacturing, specialized cooling systems are used to maintain process fluid temperatures to ensure product quality and safety.Thermal Energy Storage Systems :
These systems store excess thermal energy during off-peak times and release it when needed, helping to manage energy demand and costs.Selecting the right industrial process cooling solution depends on factors such as the type of process, cooling capacity, temperature requirements, energy efficiency goals, and environmental considerations. Engineering expertise is crucial to designing, implementing, and maintaining an effective cooling solution tailored to the specific needs of each industrial application.
Industrial process cooling plays a critical role in a wide range of applications across various industries. Cooling solutions are used to manage and dissipate heat generated during industrial processes, ensuring efficient operation, product quality, and equipment reliability. Here are some common industrial process cooling applications :
Manufacturing Processes :
Chemical reactions often release heat, which can be detrimental to reaction kinetics and product quality. Cooling solutions are used to control temperatures during chemical processes, ensuring safe and efficient reactions.Chemical Processing :
Chemical reactions often release heat, which can be detrimental to reaction kinetics and product quality. Cooling solutions are used to control temperatures during chemical processes, ensuring safe and efficient reactions.Power Generation :
In power plants, cooling is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of turbines, generators, and other equipment. Cooling systems help dissipate heat from power generation processes, such as steam turbines.Data Centers and IT Equipment :
Cooling is vital to prevent data centers and IT equipment from overheating. Precision cooling systems maintain stable temperatures, ensuring the reliability of servers, networking equipment, and other electronics.Pharmaceutical Production :
The pharmaceutical industry requires precise temperature control to ensure the quality and safety of medications. Cooling is used in various stages, including drug synthesis, purification, and formulation.Food and Beverage Processing :
Cooling is employed in food and beverage industries to control the temperature of ingredients, processes, and products. It helps extend shelf life, maintain freshness, and meet regulatory requirements.Plastics and Rubber Industries :
Cooling is essential in plastic injection molding and rubber extrusion processes. Proper cooling ensures that molded products solidify correctly and maintain their desired shapes.Semiconductor Manufacturing :
The semiconductor industry requires precise temperature control to ensure the quality of integrated circuits. Cooling is used during various fabrication steps, including etching, deposition, and lithography.Automotive Manufacturing :
Cooling systems are integral to automotive manufacturing processes, such as engine assembly and paint shops. They help maintain tolerances, prevent warping, and control surface finishes.Medical Device Production :
In medical device manufacturing, cooling is used to ensure the quality and precision of products such as medical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment.Printing and Packaging :
Cooling is important in printing and packaging industries to maintain consistent product quality and avoid issues like ink smudging and substrate deformation.Textile Production :
Cooling is used in various stages of textile production to control dyeing, printing, and finishing processes, ensuring color fastness and material integrity.Aerospace and Defense :
Cooling is employed in aerospace applications to manage heat generated during machining, welding, and other processes. It also helps maintain stable conditions for testing and assembly.These are just a few examples of how industrial process cooling is integral to diverse industries. Cooling solutions are customized based on specific process requirements, temperature ranges, cooling capacities, energy efficiency goals, and environmental considerations in each application.
Working Principle, Advantages, Disadvnatages, Application & Room Condition
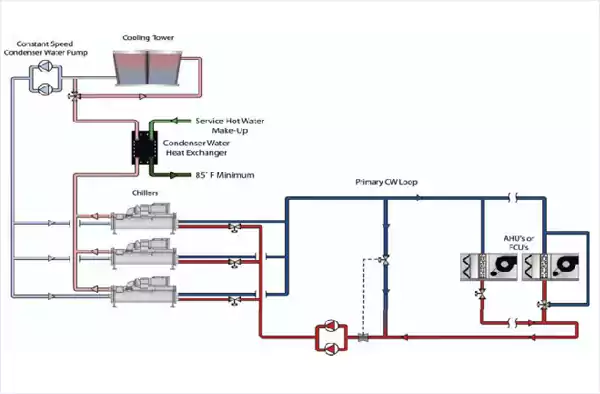
Chiller with Open Type Single Expansion Tank
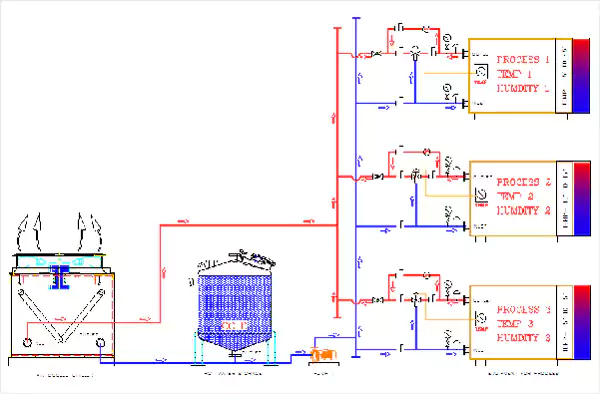
Chiller with Single Pressurised Expansion Tank
Chiller with Open Type Hot Well and Cold Well
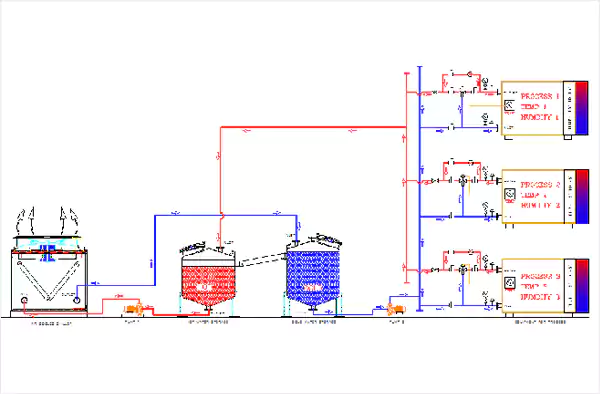
Chiller with Secondary Variable
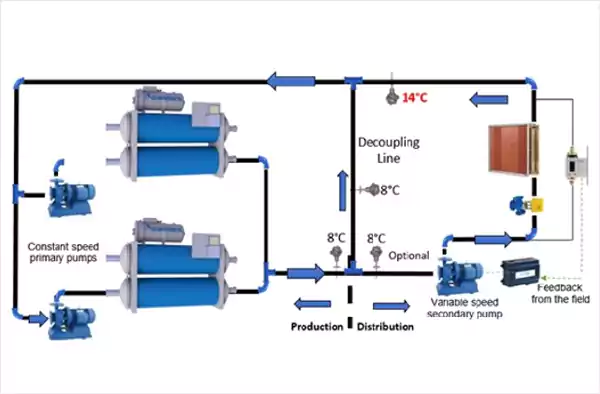
Chiller with Fixed Flow
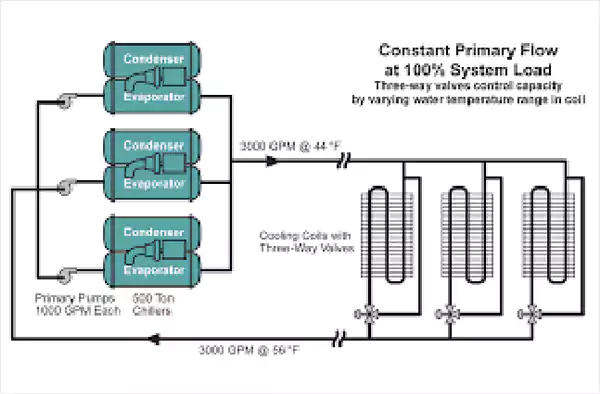
Chiller with Portable Skid
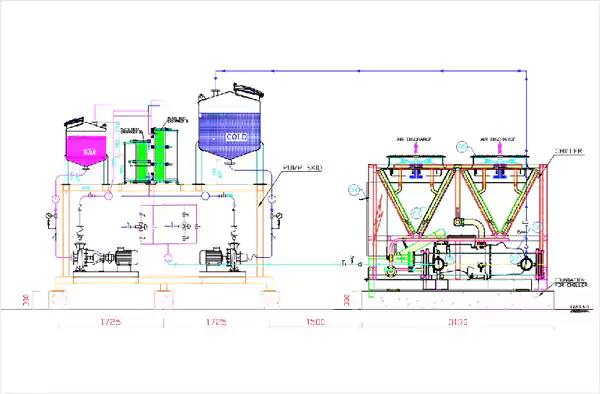
Chiller with Primery Variable
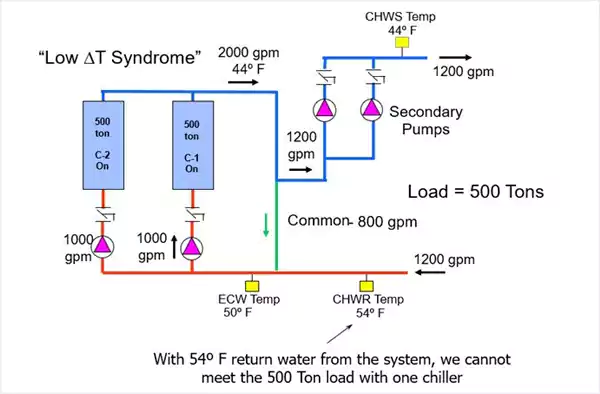
Chiller Plant with Chilled Water Heat Recovery
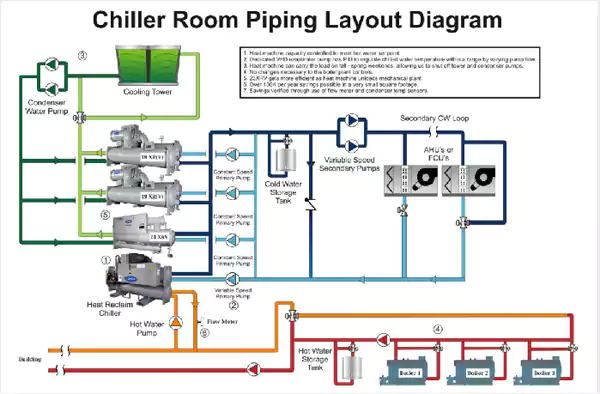
Water Cooled with 100% Fresh Air AHU Heat Recovery
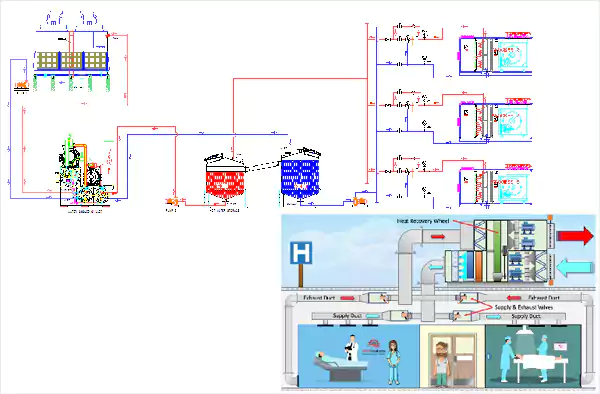
AHU with Fixed Speed Compressors

AHU with Variable Speed Compressors
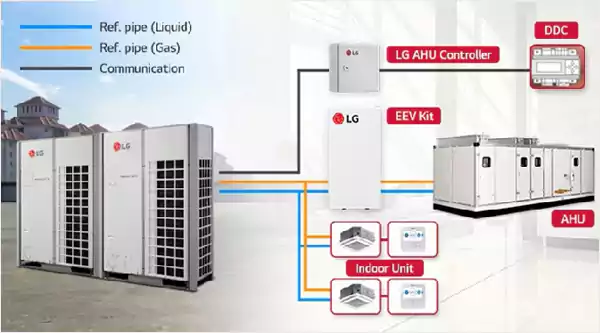
Variable Refrigerant Flow System
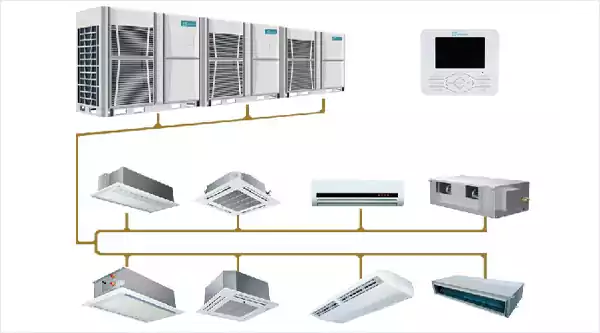
Water Cooled with Condesation Based Dehumidfication
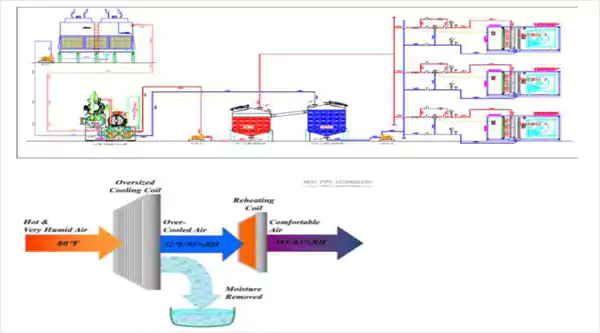
Water Cooled with Absorption Based Dehumidfication
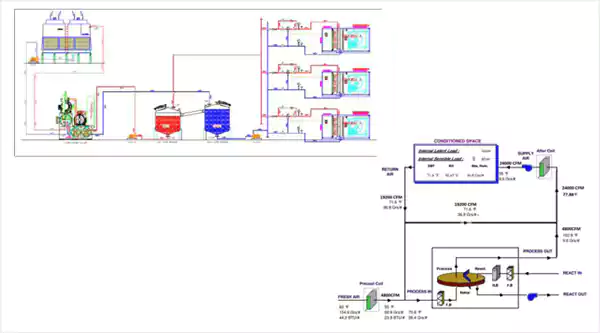
Water Cooled with Multi Indoors
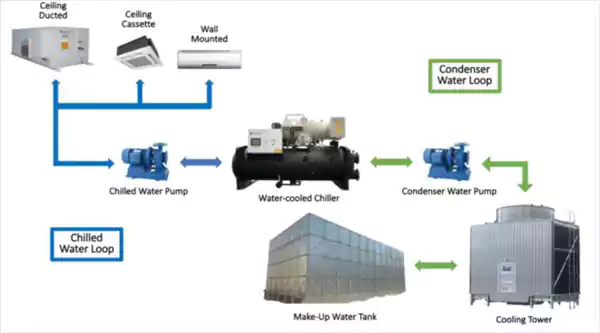
Cooled with AHU
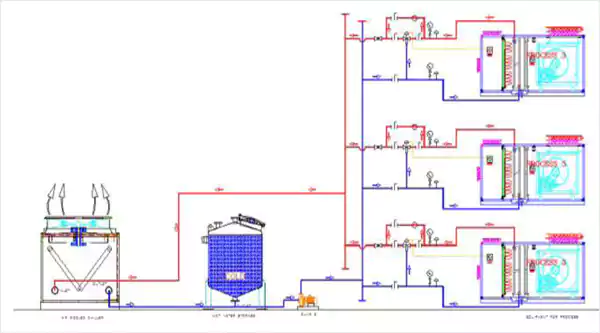
Air Cooled with 100% Fresh Air AHU with Heat Recovery
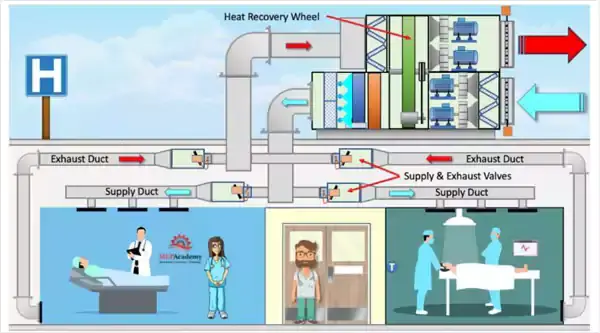
Air Cooled with and Down Risers
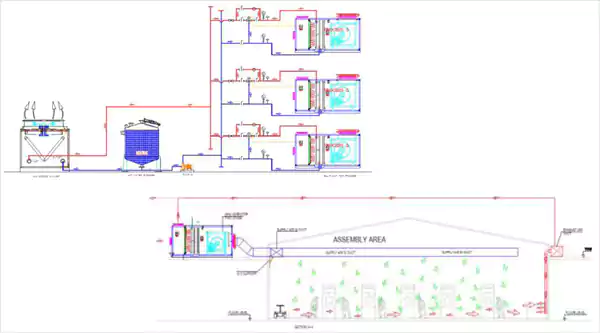
Working Principle, Advantages, Disadvnatages, Application & Room Condition
Chiller with Open Type Single Expansion Tank
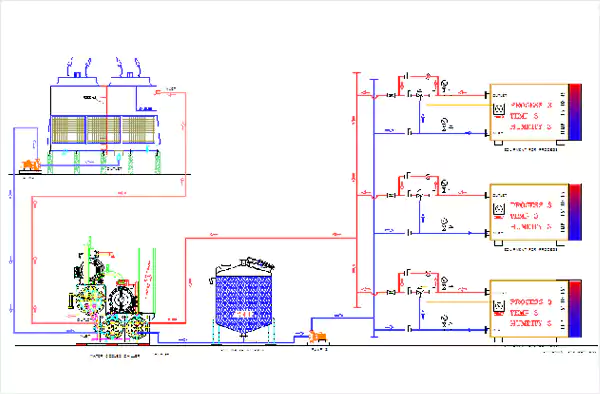
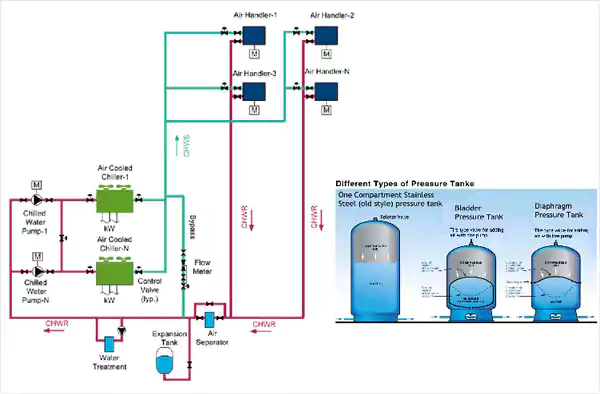
Chiller with Single Pressurised Expansion Tank

Chiller with Pressurised Expansion Tank, Air Seperator & Auto Tube Cleaning Systems

Chiller with Open Type Hot Well and Cold Well
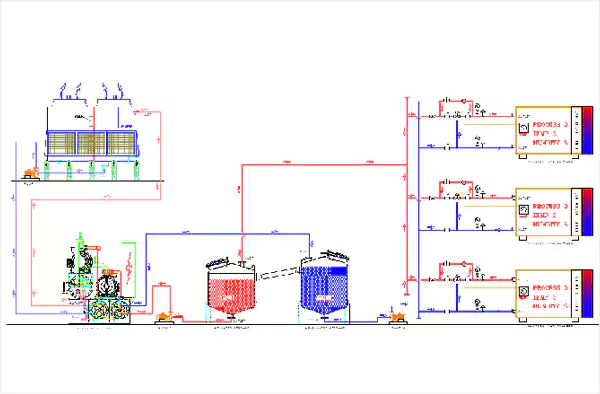
Chiller with Primery Variable

Chiller with Secondary Variable

Chiller with Fixed Flow

Chiller with Portable Skid

Chiller Plant with Chilled Water Heat Recovery

Chiller with Condensor Water Heat Recovery